Biodiesel (FAME/UCOME)
Biodieselis generally defined as fuel produced by chemical processes such as esterification, neutralization, water washing, and distillation of animal and vegetable oil or used cooking oil. It is cons
Biodieselis generally defined as fuel produced by chemical processes such as esterification, neutralization, water washing, and distillation of animal and vegetable oil or used cooking oil. It is cons
Ester based biodiesel (FAME/UCOME): First generation biodiesel, narrowly defined as biodiesel. Specifically, it refers to the process of producing biodiesel through ester exchange, where the fatty acid triglycerides in animal and plant fats, gutter oil, and other raw materials undergo ester exchange reaction with small molecule alcohols (mostly methanol) to generate the corresponding fatty acid methyl ester, which is then subjected to appropriate processing such as separating glycerol, washing with water, and drying. The first generation diesel technology is mature and is currently the main variety of biodiesel both domestically and internationally. The first generation biodiesel ester exchange method can be divided into acid or base catalytic method, biological enzyme method, and supercritical method based on its reaction characteristics, among which acid or base catalytic method is currently more commonly used. From the perspective of physical and chemical properties, the first generation of biodiesel has disadvantages such as poor low-temperature fluidity and unsuitable for long-term storage. Therefore, the first generation of biodiesel needs to be mixed with diesel for use, with a blending ratio usually between 2% and 20%.
Ester based biodiesel production process:
1. Collect used cooking oil: Collect used cooking oil from kitchen waste treatment centers, catering enterprises, and other places.
2. Filtration and pretreatment: The collected used cooking oil is filtered to remove impurities, solid particles, etc., and subjected to pretreatment such as deacidification, water removal, etc. to improve the stability of the catalyst in subsequent reactions.
3. Esterification reaction: The pre treated used cooking oil is esterified with alcohol (such as methanol) in the presence of a catalyst to produce methyl ester (biodiesel) and glycerol.
4. Neutralization and Separation: Neutralize the mixture after esterification reaction, add an appropriate amount of acid, alkali and other chemical substances to separate glycerol and biodiesel.
5. decolorization and purification: decolorize the separated biodiesel to remove impurities and colors, resulting in a purer quality.
6. Dehydration and acid removal: Further remove moisture and acidic substances from biodiesel to ensure its stable quality.
7. Dehydration and distillation: Through distillation and other processes, volatile substances such as solvents and impurities in biodiesel are removed to improve its purity.
8. Refining and additive treatment: Refine biodiesel, such as decolorizing and deodorizing operations, and add additives such as antioxidants and preservatives to improve its stability and service life.
9. Quality inspection and storage: Conduct quality testing on biodiesel to ensure it meets relevant standard requirements, and then store and package it for sale or use.
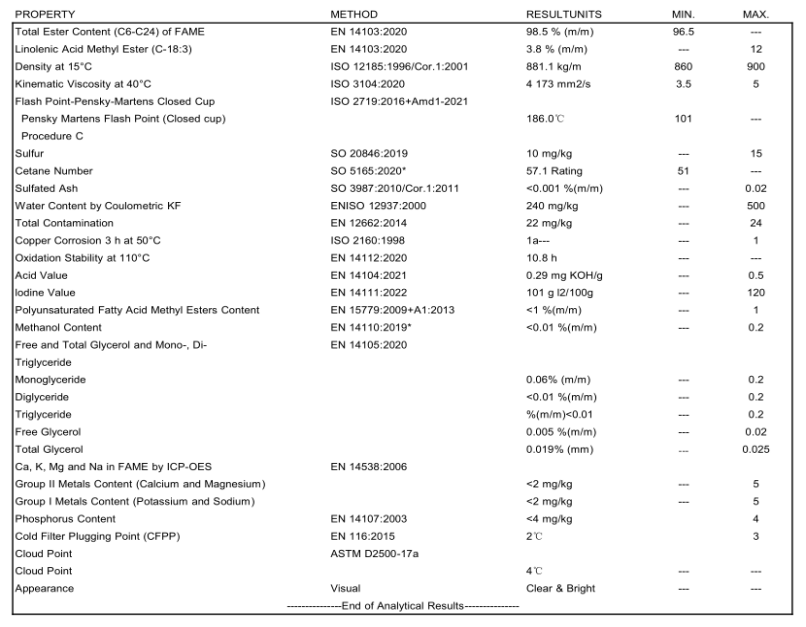
Quality Index:


+86 19113264742
Room G755, Office Building 2, Bonded Port Area, Xinying Bay District, Yangpu Economic Development Zone, Hainan Province.
09:00-18:00